THE INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Indus Valley Civilization and it’s Discovery
The Early age of Indian history starts with the birth of the Indus Valley
Civilization (IVC), also known as Harappan Civilization.
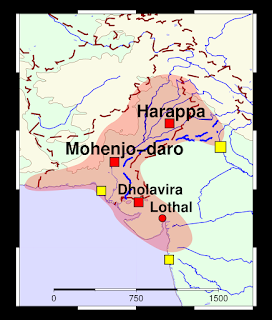
- The Indus River Valley Civilization, 3300-1300 BCE, also known as the Harappan Civilization, extended from modern-day northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India.
- The Indus Valley was home to the largest of the four ancient urban civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, India and China.
- In 1856, British colonial officials in India were busy monitoring the construction of a railway connecting the cities of Lahore and Karachi in modern-day Pakistan along the Indus River valley.
- As they continued to work, some of the labourers discovered many fire-baked bricks lodged in the dry terrain. There were hundreds of thousands of fairly uniform bricks, which seemed to be quite old. Nonetheless, the workers used some of them to construct the road bed, unaware that they were using ancient artifacts.
- In 1920s, the Archaeological Department of India
carried out excavations in the Indus valley wherein the ruins of the two
old cities, Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa were unearthed.
- In 1924, John Marshall, Director-General of the ASI, announced the discovery of a new civilization in the Indus valley to the world.
What was Special about these cities?
· In some cities, special buildings were constructed on the citadel. For example, in Mohenjo-Daro, a very special tank, which archaeologists call the Great Bath, was built in this area.
· Other cities, such as Kalibangan and Lothal had fire altars, where sacrifices may have been performed.
· some cities like Mohenjo-Daro, Harappa, and Lothal had elaborate store houses.
Mohenjo-Daro became not only the largest city of the Indus
Valley Civilization but one of the world’s earliest major urban centers.
The remarkable thing about the arrangement of the
houses in the cities is that they followed the grid system.
THE GRID SYSTEM
· Granaries constituted an important part of the Harappan cities.
·
The drainage system of
Mohenjo-Daro was very impressive. Very often, drains in houses
were connected to those on the streets and smaller drains led into bigger ones.
As the drains were covered, inspection holes were provided at intervals to
clean them.
A Street In Mohenjo-Daro With a Drain and Well
· In almost all cities every big or small house had its own courtyard and bathroom.
Harappan
Agriculture
· The Harappan villages, mostly situated near the flood plains, produced sufficient foodgrains.
· Wheat, barley, rai, peas, sesame, lentil, chickpea and mustard were produced. Millets are also found from sites in Gujarat. While rice uses were relatively rare.
· The Indus people were the earliest people to produce cotton.
· Most Harappan sites are located in semi-arid lands, where
irrigation was probably required for agriculture.
· Although the Harappans practised agriculture, animals were also conserved on a large scale.
New crafts in the city
· Most of the things that
have been found by archaeologists are made of stone, shell and metal, including
copper, bronze, gold and silver.
· Copper and bronze were
used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used
to make ornaments and vessels.
· The Harappans practised boat-making and seal-making.
· Terracotta manufacture was also an important craft.
· The potter's wheel was in full use, and the Harappans
produced their own characteristic pottery, which was glossy and shining.

Religion, Writings and Culture
· The Indus script remains indecipherable without any comparable symbols, and is thought to have evolved independently of the writing in Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt. Researchers are using technological advances in computer science in order to attempt to decipher it.
· The Harappan religion also remains a topic of
speculation. It has been widely suggested that the Harappans worshipped a
mother goddess who symbolized fertility. In contrast to Egyptian and Mesopotamian
civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization seems to have lacked any temples
or palaces that would give clear evidence of religious rites or specific
deities.
· The male deity is represented on a seal with three
horneheads, represented in the sitting posture of a yogi.
The God is surrounded by an elephant, a tiger, a rhinoceros, and has a buffalo below his throne. At his feet appear two deer.The depicted god is identified as Pashupati Mahadeva.
· No temples have been found at any Harappan sites but people used to worship nature as the supreme power.
Decline of the Indus Valley Civilization
· There are several factors for decline of the Indus Valley Civilization.
· In later cultures, various elements of the IVC are found which suggest that civilization did not disappear suddenly due to an invasion.
· On the other hand, many scholars believe natural factors are behind the decline of the IVC.
o The natural factors could be geological and climatic.
o It is believed that the Indus Valley region experienced several natural disturbances which causes earthquakes. Which also changed courses of rivers or dried them up.
o Another natural reason might be changes in patterns of rainfall.
· There could be also dramatic shifts in the river courses, which might have brought floods to the food producing areas.Due to combination of these natural causes there was a slow but inevitable collapse of IVC.
Blog Credits : Suyash Deulgaonkar
References : http://asiegov.gov.in/
ttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harappa#:~:text=The%20Harappan%20Civilisation%20has%20its,valley%20in%20Punjab%20and%20Sindh.
NOTE :- This blog is meant for Educational Purpose only .We do not own any Copyrights related to images and information , all the rights goes to their respective owners . The soul purpose of this blog is to Educate, Inspire, Empower and to create awareness in the viewers. The usage is non-commercial(Not For Profit) and we do not make any money from it.
h












Comments
Post a Comment